Goods and Services Tax (GST) Policy
1. Purpose
The CIT Goods and Services Tax (GST) Policy provides guidance to ensure compliance with the requirements of the A New Tax System (Goods and Services Tax) Act 1999 (The GST Act).
2. Scope
The Policy applies to all officers of CIT and specifically, to all relevant accounts payable and accounts receivable transactions undertaken by, for, or on behalf of CIT.
3. Principles
3.1 CIT is an entity that is required to remit/pay GST and collect GST on a range of financial transactions. Transactions with a GST component are netted off to result in either a net GST payable or receivable to/from the Australian Taxation Office (ATO) from month to month.
GST types as applicable to CIT under the GST Act include:
- Taxable supplies;
- Non-Taxable (GST free) supplies (including for exports);
- Input taxed supplies; and
- Out of scope transactions.
A sale is not a taxable supply if it is GST free or input taxed.
3.2 Taxable Supplies
CIT is registered with the ATO for GST, and to be considered as a taxable supply, a given transaction will:
- Require a payment (not always a monetary payment) to a third party;
- Be made in the course of undertaking business activities;
- Be connected with Australia (see more detailed rules in ATO publications); and
- Require the recording of the GST component of the transaction in the (Oracle) accounting system and to be coded in the accounts as 10% AR and the GST coded as a (net) payable in the Oracle general ledger account 310612.
A taxable supply can arise from vouchers such as mobile phone top up cards. The applicable input tax credit may be claimed when the value of the voucher transaction is utilised.
Surcharges may also have GST implications as dependent on the type of supply. Surcharges can apply to credit cards and service charges may also be levied on given supplies.
3.3 Non-Taxable Supplies
GST free supplies do not include GST in the price/charge. CIT claims credits for GST included in the price of taxable purchases where those purchases are used to make GST free supplies. GST free items include most basic foods, some education courses, some medical and healthcare services, some utilities costs (water, sewerage and drainage), international transport and some childcare services.
3.4 Education Courses
Division 38-C-Education of the GST Act is of particular relevance to CIT in regards to GST free transactions. Items which are GST free for CIT include:
- Course fees for most tertiary courses;
- Course fees for approved English language courses;
- Course materials for a subject undertaken in a GST free education course;
- Student administration service fees directly related to a GST free course; and
- Excursions or field trips directly related to the curriculum of an education course and by nature, are not predominantly recreational.
3.5 Recognition of Prior Learning
CIT's charge for the assessment or issue of qualifications for the purpose of access to education are GST free transactions and are coded as Free AR transactions.
3.6 Mixed Supplies (Sales)
Some sales may be partly taxable and partly GST free or input taxed. These sales are termed mixed supplies.
In some instances, a given sale may include items which attract GST and items which are GST free. In this case the items may need to be separately coded, e.g. for an invoice that has a number of different foods. As an example, bottled water will be GST free, however a processed/soft drink (e.g. Lemonade) will be a taxable item.
3.7 Supplies (Sales) Not GST-Free
The following supplies related to an education course are not GST free:
- Items that are not directly related to education courses or are not course materials. These items could be a supply by way of a sale, lease or hire of goods;
- CITSA Membership; and
- Textbooks.
Transactions with the above characteristics are coded to 10% AR and the GST is coded to the GL payables account, 310612.
3.8 Input Taxed Supplies
An example of an input taxed sale for CIT, is student accommodation rent. CIT manages student accommodation facilities for which it receives rent and this revenue is input taxed, i.e. no GST is included in the rent charged and CIT may not claim the GST it has incurred for expenses such as repairs and maintenance costs.
GST is not included in the price of input taxed sales made and CIT cannot claim GST credits for purchases undertaken to make input taxed supplies. Rental transactions with the above characteristics are coded to Input Tax AR. Purchasing transactions with this characteristic are coded to Input Tax AP.
3.9 Out of Scope Transactions
An out of scope transaction is one which does not relate to a supply or sale in the context of the GST Act.
Examples of items that are not deemed to be a supply or sale in this context include:
- Government appropriations;
- Other appropriations where the monies received are not consideration for any supply;
- Research grants from approved bodies;
- Donations, bequests, prizes, sponsorships and scholarships (provided they are made voluntarily, there is no expectation of receiving anything in return and there is no material benefit to the donor);
- Dividends;
- Parking fines; and
- Internal transactions between operational units.
3.10 Taxable and Creditable Importations
Importation of goods such as learning materials or a teaching software application may give rise to a requirement to pay GST and/or claim an input tax credit.
A taxable importation occurs when:
- Goods are imported;
- The goods are entered for home consumption - as defined in the Customs Act 1901; and
- The importation is not excluded from being taxable because it is a 'non-taxable importation'.
In this case, CIT is liable to pay the GST on the taxable importation. A creditable importation occurs when:
- Goods are imported for a creditable purpose;
- The importation is a taxable importation; and
- The importer is registered or is required to be registered for GST.
'Creditable purpose' means as part of carrying on an enterprise, but not for making input taxed supplies or for private or domestic purposes. An input tax credit may be claimed by CIT when the three creditable importation criteria are met.
3.11 GST Credits
CIT can claim GST credits for the GST included in a given purchase where:
- A tax invoice is provided by the supplier;
- The price includes and specifies a GST component;
- The purchase is solely or partly for the purposes of carrying on CIT operations; and
- Is accompanied by a specific obligation to pay for the item purchased.
Transactions with these characteristics are coded to 10% AP (or to 10% Cap AP for capital acquisitions) and the GST is coded to the GL receivables account 111285. CIT cannot claim GST credits for purchases that are made for private purposes and in any case, such purchases should not be undertaken.
3.12 Valid Tax Invoice
In order to claim a GST credit for purchases that cost more than the GST inclusive amount of $82.50, a valid tax invoice is required (the GST exclusive expense being $75 and the GST component $7.50).
Requirements of tax invoices
Tax invoices for taxable sales of less than $1,000 must include information to clearly confirm:
- that the document is a Tax Invoice;
- the seller's identity;
- the seller's Australian Business Number (ABN);
- the date the invoice was issued;
- a brief description of the items sold, including the quantity (if applicable) and the price;
- the GST amount (if any) payable where this can be shown separately or, if the GST amount is exactly one-eleventh of the total price, a statement such as 'Total price includes GST';
- the extent to which each sale (i.e. as shown on each line) on the invoice is a taxable sale (that is, the extent to which each line includes GST); and
For Tax Invoices for sales of $1,000 or more a further element is required to be confirmed, that being: - the buyer's identity or ABN.
3.13 Business Activity Statement (BAS) Requirements¹
Data for calculating the amount owed to or due to be received from the ATO is sourced from the Accounts Receivable (AR) and Accounts Payables (AP) sub-ledgers and the General Ledger (GL).
AP transactions are (most often) entered by officers at Shared Services Finance based on coding decisions made by CIT Officers.
AR transactions enter into the sub-ledger in a variety of ways, including from external systems and journals. Transaction coding is also undertaken in a variety of ways.
Journals are prepared by CIT Finance Officers, and by the Shared Services General Finance or Reporting team(s).
The Oracle finance system has a BAS module which extracts tax related data from the Accounts Receivable and Payable sub-ledgers and the General Ledger.
The monthly BAS is managed through the "Onesource" GST system managed by Shared Services. Data from the Oracle financial system is uploaded into Onesource for the purposes of BAS preparation and reconciliation activities.
The reconciliation process can be problematic if tax coding errors have been made in any of the process environments. Errors must be corrected by GL journal in the current or subsequent month in order to prevent incorrect opening and closing balances in tax accounts.
When BAS calculations are completed and as applicable, inconsistencies are resolved, the net amount of GST payable to or receivable from the ATO is entered through an online facility (via an "Auskey"² function) and if a payment is required (i.e. if GST collected on sales exceeds GST paid on supplies), a payment to the ATO is arranged through the AP process.
Paying the BAS for the previous month by the 21st day of the next month is a KPI (Key Performance Indicator) for Shared Services.
¹ Refer to the following link for example invoices: (https://www.ato.gov.au/Business/GST/Tax-invoices/)
² A secure login methodology that identifies the user when utilising government online services.
3.14 Tax Codes
The following tables list the Tax codes as applicable to Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable.
Tax Codes for Sales (Accounts Receivable)
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 10% AR | Revenue receipts that include a GST component. |
| Free AR | Revenue receipts that do not have a GST component as they are "GST Free" under GST legislation. |
| Input Tax AR | Input taxed supply relates to transactions which are covered by specific provisions in the GST Act, e.g. financial supplies, interest, and residential accommodation. |
| Outside AR | The supply is outside the scope of the GST legislation therefore the transaction is not included in the Business Activity Statement. |
Tax Codes for Procurements (Accounts Payable)
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 10% AP | Acquisition of goods and services that are subject to GST and for which an input tax credit is to be claimed. To be applied to a valid Tax Invoice.. |
| Free AP | Acquisition of goods and services that are not subject to GST. Examples include most hospital, medical and pharmaceutical supplies, most foods, education, child care, water and sewerage charges (specifically proclaimed to be 'GST Free' under GST legislation). |
| Input Tax AP | Acquisition of goods and services that are subject to GST, but for which an input tax credit cannot be claimed, e.g. financial supplies and supplies of residential accommodation. |
| Exempt | Acquisition of goods and services that are not subject to GST as the supply is exempt under Division 81. |
| Outside AP | The supply of goods and services is outside the scope of the GST legislation, e.g. salaries, suppliers not registered for GST, payroll tax and overseas payments. |
| No ABN Withhold | Purchase of goods and services for which an ABN is required but is not quoted. Withholding tax is applicable unless a Declaration by Supplier form is completed (withheld at the rate of 49% of the total payment). |
| Capital 10% | Acquisition of capital goods and services subject to GST and for which an input tax credit is to be claimed. This usually applies to asset acquisitions. |
| Free CAP | Acquisition of goods and services of a capital nature that are not subject to GST (Specifically proclaimed to be 'GST Free' under GST legislation). |
| Input CAP | Acquisition of goods and services (of a capital nature) that are subject to GST, but for which an input tax credit cannot be claimed. |
3.15 Examples of GST Transactions
Invoice example - Free AP
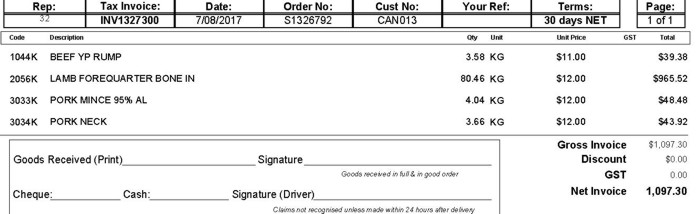
An example of a purchase of a food which is not subject to GST. When completing the Accounts Payable Invoice Cover Sheet, ensure that the tax code used in the GST Tax Type Column is Free AP and the GST Amount is $0.00.
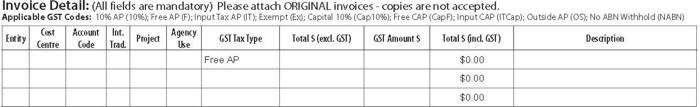
Invoice example - GST applicable

An example of a payment made for a service which includes GST.
The tax code to use in the Accounts Payable Invoice Cover Sheet GST Tax Type Column is 10% AP and the GST amount is $4.00
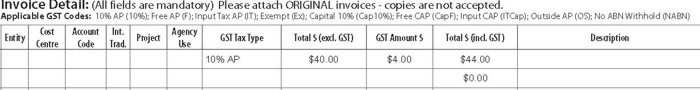
Invoice example - mixed GST supplies
In some instances, an invoice will be received with items that attract GST and some that do not. In the example below, items with an * contain GST which amount to $0.86. The remaining lines do not attract GST.

In completing the Accounts Payable Invoice Cover Sheet, the GST Codes to be entered in the GST Tax Type will be Free AP and 10% AP. The entries will be on separate lines as per below.
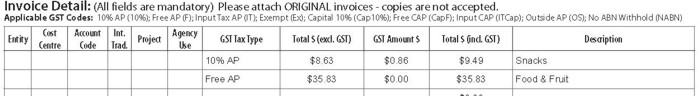
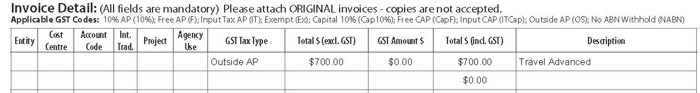
Invoice example - Travel Advance (Outside AP)
In this instance an advance is made to a staff member who is to undertake international travel. The Accounts Payable Invoice Cover Sheet GST Tax Type Code to use is Outside AP.
4. Documentation
- A New Tax System (Goods and Services Tax) Act 1999
- Customs Act 1901
- Financial Management Act 1996
- Finance Policy (CIT)
- Fringe Benefits Tax Guide ATO
- Financial Delegations Schedule (Internal CIT Staff link)
- Shared Services GST Policy
5. Definitions
All terminology used in this policy is consistent with definitions in the CIT Definitions of Terms.
6. Policy Contact Officer
For more information or for queries that are unable to be addressed through regular channels, please contact a Business Support Manager, Financial Services or the Senior Director, Finance.
Contact CIT Student Services on (02) 6207 3188 or email infoline@cit.edu.au for further information.
7. Procedures
This policy is implemented through the associated procedures. The Procedures cover all transactions conducted by, for, and on behalf of CIT. Authority to make changes to the procedures rests with the policy owner.
| POLICY INFORMATION |
|
Policy No: 2019/1890 Approved: June 2022 Next Review: August 2023 Category: Corporate policies Policy Owner: Executive Director, Corporate Services |
| PROCEDURES/DOWNLOADS |
(PDF File 157.0 KB) |
| POLICY SEARCH |
| POLICY RESOURCES |
| Browse Policies CIT Definition of Terms CIT Governance Framework (PDF 381Kb) Complaints Form Client Service Charter (PDF 845Kb) Student Code of Conduct (PDF 286Kb) |
| POLICIES LAST UPDATED |
|
01 Apr 2025: Training and Assessment Policy 01 Apr 2025: Training and Assessment Strategy (TAS) Development Policy 20 Mar 2025: Academic Dress Policy 25 Feb 2025: Assessment Validation Policy 24 Feb 2025: Assessment Policy |

